
Sodium acid pyrophosphate, often abbreviated as SAPP, is a common food additive. It plays a crucial role in the food industry.
This compound is widely used in baking powders and processed foods. It helps maintain color and texture in various products.
SAPP is also known by other names, such as disodium pyrophosphate. It is a white, water-soluble powder with a slightly acidic taste.
Understanding its uses and benefits can help consumers make informed choices. However, it's important to be aware of potential dangers and side effects.
In this guide, we will explore the many facets of sodium acid pyrophosphate.
Sodium acid pyrophosphate, or SAPP, is a type of phosphate salt. It is used as a leavening agent in the baking industry.
This compound is particularly valuable for its role in processed foods. It helps adjust pH levels, which is crucial for maintaining food quality.
SAPP is part of a broader group of phosphates. These are essential for a variety of functions in food processing. Key attributes of SAPP include:
● White and water-soluble
● Slightly acidic taste
● Provides texture in food products

These properties make it a staple ingredient in numerous food products.
Sodium acid pyrophosphate is synthesized through a chemical reaction involving sodium dihydrogen phosphate. The process requires controlled heat, converting it into SAPP.
During production, careful temperature regulation is essential. This ensures the compound maintains its purity and desired properties.
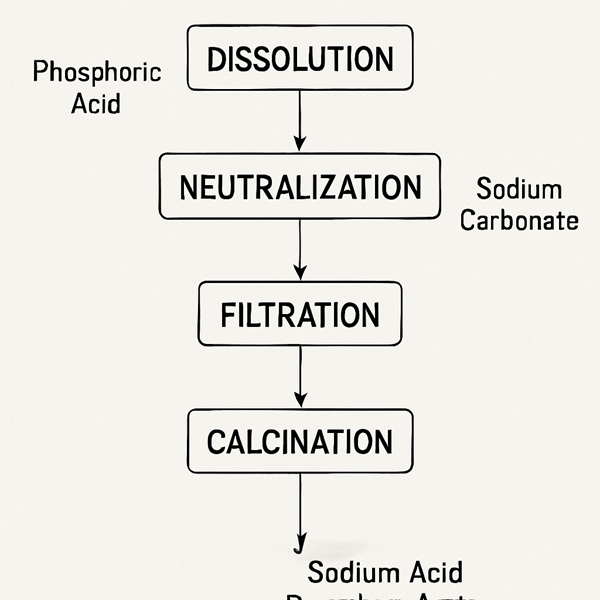
This manufacturing process provides a stable and effective ingredient for various industrial and food applications. The precise synthesis method underscores its widespread use.
Sodium acid pyrophosphate is also known by other names. Commonly, it is referred to as disodium pyrophosphate or disodium dihydrogen pyrophosphate. These names highlight its chemical structure and composition.
Its chemical properties include being a white, water-soluble powder with a slightly acidic taste. The key characteristics of sodium acid pyrophosphate include:
● Solubility in water
● Slightly acidic
● White powder form
Sodium acid pyrophosphate (SAPP) is widely used in the food industry. Its primary role is as a leavening agent. This helps baked goods rise by releasing carbon dioxide.
SAPP is critical for maintaining food texture and color. It prevents potatoes from discoloring and improves the quality of canned seafood.
The food industry utilizes SAPP to control the acidity in products. It also functions as an emulsifier and stabilizer.
Common uses include:
● Baked goods
● Processed meats
● Canned seafood

SAPP is a key ingredient in baking powder. This allows baked products to rise properly and stay fluffy. Its slow-release properties are crucial for even texture in goods like cakes and bread.
In baking, SAPP also helps with moisture retention. This ensures that baked items remain fresh and soft after baking. Key uses include:
● Baking powder formulations
● Cakes and pastries

Beyond baking, SAPP is used in various other foods. It enhances the quality and shelf life of many products. In seafood, SAPP helps retain moisture and improves texture. In potato products, it prevents discoloration.
In the meat industry, SAPP is used for moisture retention. This is crucial for processed meats like sausages. Important applications include:
● Canned seafood
● Processed potatoes
● Cured meats

Sodium acid pyrophosphate offers several benefits in food production. It enhances the quality of food by improving texture and appearance. This leads to longer shelf life and more appealing products.
SAPP is also an effective pH stabilizer, which is essential for taste consistency. This helps in keeping processed foods fresh longer. Notable benefits include:
● Improved texture and stability
● Enhanced food appearance
● Effective pH control
Sodium acid pyrophosphate is generally recognized as safe by food safety authorities. The FDA includes it in their list of approved food additives. When used within recommended limits, SAPP poses minimal health risks.
However, some people may have sensitivities to phosphates. These individuals should monitor their intake of foods with SAPP. Awareness of food labels can help manage this.
Excessive consumption could lead to health issues like mineral imbalances. It is crucial to stick to advised quantities. Safety considerations include:
● FDA approval as GRAS
● Importance of regulated usage
● Potential concerns for sensitive individuals
While sodium acid pyrophosphate is safe in regulated amounts, it can have side effects. Overconsumption may affect mineral balance in the body. People with phosphate sensitivity need extra caution.
To avoid adverse effects, it's important to follow guidelines. Awareness of SAPP presence in food can help manage risks. Potential issues include:
● Mineral imbalances from excessive consumption
● Phosphate sensitivity reactions
● Increased sodium levels in the diet
Sodium acid pyrophosphate is recognized as safe by key food authorities. The FDA lists it as generally recognized as safe (GRAS). Its use in regulated amounts ensures consumer safety.
Food labels often list SAPP as a common ingredient. Consumers should look for:
● “Sodium acid pyrophosphate”
● “Disodium pyrophosphate”
● “Disodium dihydrogen pyrophosphate”
Staying informed about these labels helps avoid overconsumption.
Many people have questions about sodium acid pyrophosphate. Understanding its role in food can ease concerns. Below are common queries answered:
● What is SAPP used for?
It's used in baking, processed foods, and as a leavening agent.
● Is it safe for consumption?
Yes, when used within regulated levels.
These answers clarify common concerns. Always refer to trusted sources for detailed information.
Sodium acid pyrophosphate (SAPP) plays a vital role in the food industry. Its unique acidic properties make it an indispensable leavening agent, setting it apart from other phosphate stabilizers like Tetrasodium Pyrophosphate (TSPP). SAPP helps improve texture, color, and shelf life. While it’s safe in regulated amounts, it’s crucial to check labels for those sensitive to phosphates. Understanding SAPP helps consumers make informed food choices and ensures you select the correct ingredient for your specific baking or processing application.