
In the field of wastewater treatment, technical terminology can sometimes obscure relatively simple concepts. Among the most misunderstood terms are coagulation, flocculation, and coagulant chemicals. This article will break down these terms, explain their relationships, and clarify how to properly use common treatment agents such as coagulants, flocculants, and coagulant aids.
Coagulation and flocculation are two sequential processes used to remove suspended particles and colloids from water. Together, they form the coagulation-flocculation process.
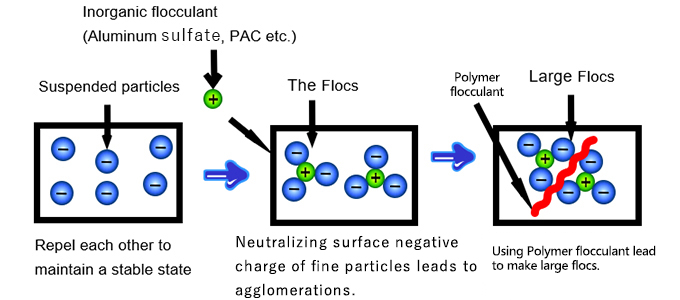
Coagulation refers to the process of destabilizing colloidal particles and very fine suspended solids in water. These particles are typically too small to settle naturally due to Brownian motion and electrostatic repulsion. By adding inorganic coagulants such as aluminum sulfate, ferric chloride, or ferric sulfate, the negative surface charges of these particles are neutralized. Once destabilized, the particles begin to cluster into larger micro-flocs.
Aluminum Sulfate (Alum) [Al₂(SO₄)₃·18H₂O]
Effective at pH 5.5–7.8, widely used in municipal and industrial wastewater treatment.
Ferric Chloride (FeCl₃)
Strong coagulant, works effectively even at lower temperatures.
Ferrous Sulfate (FeSO₄·7H₂O)
Suitable for high-alkalinity, high-turbidity water.
Once particles have coagulated into small clusters, flocculation helps form even larger aggregates called flocs or "floc particles", which can easily settle or be filtered out. This step usually involves polymeric flocculants such as polyacrylamide (PAM). These high-molecular-weight polymers bind the micro-flocs together into larger, denser flocs.
Natural polymer-based flocculants, such as modified plant gums
Coagulation = Destabilization of particles
Flocculation = Bridging and agglomeration of particles
Combined process = Coagulation–Flocculation
While the physical processes are now clear, the terminology surrounding chemicals used in these processes can be inconsistent across industries. Here’s a simplified distinction:
A coagulant is a chemical used during the coagulation stage to neutralize particle charges and initiate micro-floc formation.
A flocculant is a high-molecular-weight chemical used to form larger flocs during the flocculation stage.
Also known as a flocculation aid or blending agent, these chemicals improve the efficiency of primary coagulants. They may:
Enhance floc strength and settling speed
Adjust pH
Act as seeding agents
pH Adjusters: Lime (CaO), HCl, NaOH
Polymers: Polyacrylamide (PAM), activated silica
Oxidizers: Potassium permanganate (KMnO₄), chlorine dioxide
Inorganic particles: Clay, microsand
| Name | Chemical Formula | Main Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Sulfate (Alum) | Al₂(SO₄)₃·18H₂O | High efficiency, low cost, suitable for pH 5.5–7.8 |
| Ferric Chloride | FeCl₃·6H₂O | Works over a wide pH range (6.0–8.4), strong floc formation |
| Ferrous Sulfate | FeSO₄·7H₂O | Works well in alkaline pH, requires oxidation under acidic conditions |
| Polyaluminum Chloride (PAC) | [Aln(OH)mCl3n−m] | High adaptability, low sludge production, effective at pH 5–9 |
| Polyacrylamide (PAM) | (–CH₂CHCONH₂–)ₙ | Enhances floc formation, available in anionic/cationic forms |
| Color Removal Flocculant | Proprietary (e.g.,Polydimethyldiallylammonium chloride) | Highly cationic, ideal for dye and ink wastewater |
| Natural Polymer Flocculants | Plant-derived (e.g., F691, F703) | Eco-friendly, low cost, fast settling rate |
In practical wastewater treatment, the key is not over-analyzing terminology, but understanding how and when to apply each chemical. Whether labeled as a coagulant, flocculant, or coagulant aid, the effectiveness depends on the water characteristics and process requirements.
At TAIRAN CHEMICAL, we provide a full range of wastewater treatment chemicals, including:
Inorganic coagulants (PAC, ferric chloride, alum)
Organic flocculants (PAM, color removal agents)
Coagulant aids and pH adjusters
Need help selecting the right product? Contact us today for professional support and tailored solutions.