
Polymer acrylamide, also known as polyacrylamide (PAM), is a versatile polymer with a wide range of applications. From water treatment to agriculture, its uses are as diverse as they are essential in various industries. This article will delve into the polymerisation of acrylamide, its structure, and its myriad applications, providing a comprehensive understanding of this remarkable compound.
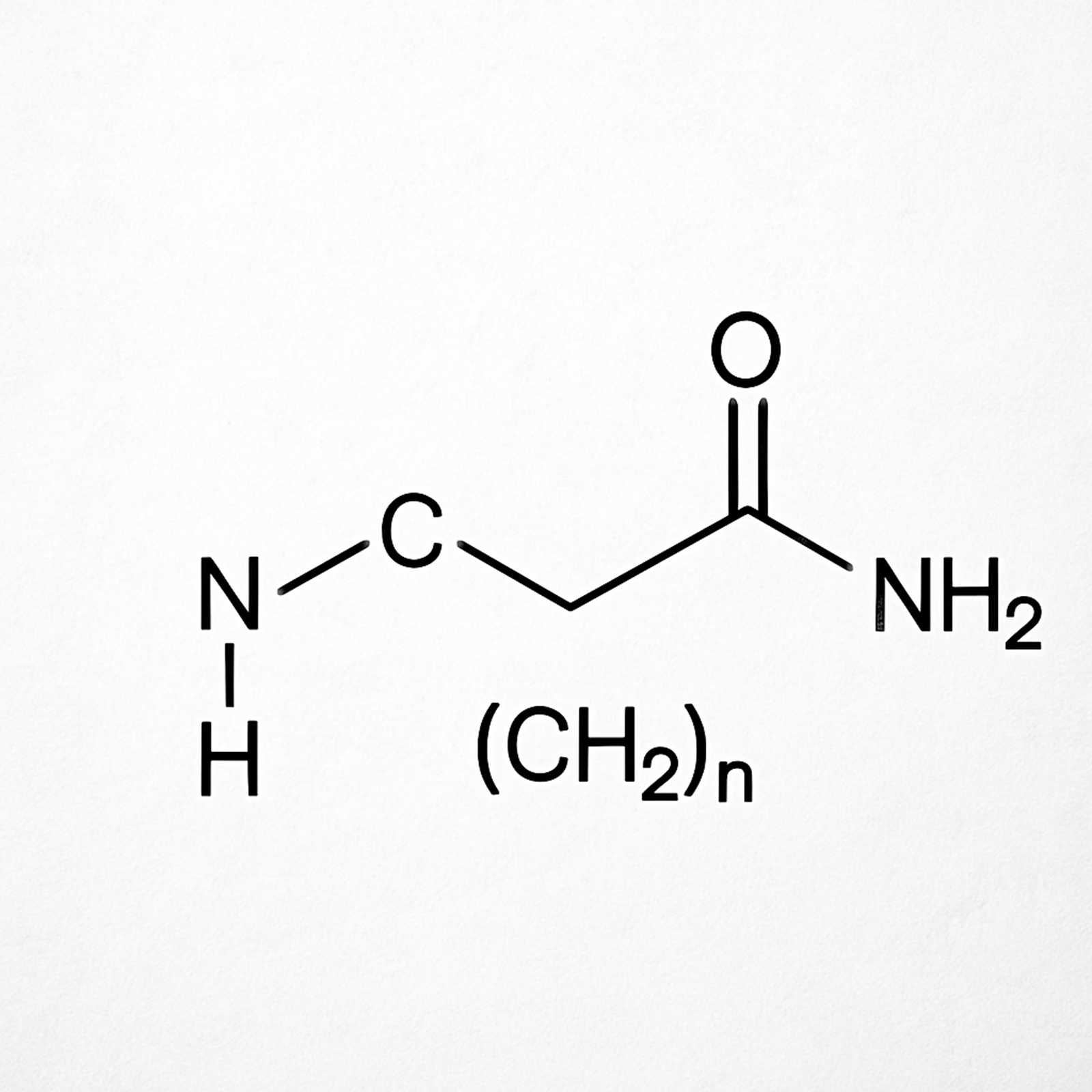
Polyacrylamide, often abbreviated as PAM, is a polymer formed from acrylamide subunits. It is widely used as a flocculant, a substance that promotes the clumping of particles, in water treatment processes. Its chemical structure consists of repeating units of the acrylamide monomer, forming long chains that are highly effective in binding particles together.
The structure of polyacrylamide is relatively simple yet efficient. Each acrylamide unit in the polymer chain contains an amide group, which is crucial for its ability to form hydrogen bonds with other molecules. This bonding capability is what makes PAM such an effective flocculant and thickening agent.
Polymerisation is the chemical process by which monomers like acrylamide are linked together to form polymers such as polyacrylamide. This process can occur through various methods, including free radical polymerization, which is the most common technique used for producing PAM.
In free radical polymerization, initiators are used to generate free radicals, which are reactive species that can start the polymerization process. These free radicals react with the acrylamide monomers, linking them together into long polymer chains. The result is polyacrylamide, a high-molecular-weight compound with significant industrial utility.
Polyacrylamide's unique properties make it suitable for a broad spectrum of applications across different industries. Here are some of the most common uses:
One of the primary applications of polyacrylamide is in water treatment. As a flocculant, PAM is used to remove suspended particles from water, making it clearer and safer for consumption. It is particularly effective in treating wastewater, where it helps in reducing the levels of turbidity and contaminants.
In agriculture, polyacrylamide is used as a soil conditioner. It helps retain soil moisture, reduces erosion, and improves the overall soil structure. By enhancing water retention, PAM supports plant growth and increases crop yields, especially in arid regions where water conservation is crucial.
The oil and gas industry utilizes polyacrylamide in enhanced oil recovery (EOR) processes. In EOR, PAM is injected into oil reservoirs to increase the viscosity of the water injected into the wells, improving the efficiency of oil extraction. This process helps in recovering more oil from the reservoir, maximizing the yield.
In paper manufacturing, polyacrylamide is used as a retention and drainage aid. It helps improve the quality of the paper by enhancing the retention of fines and fillers during the papermaking process. This results in a stronger, more consistent paper product.
The textile industry employs polyacrylamide as a sizing agent. It is used to stiffen and protect fibers during weaving, reducing breakage and improving the quality of the finished textile products.
While polyacrylamide offers numerous benefits, it is essential to consider its environmental impact. The production and use of PAM must be managed carefully to minimize potential environmental risks.
Polyacrylamide itself is considered non-toxic and biodegradable. However, its monomer, acrylamide, is a known neurotoxin and potential carcinogen. Therefore, it is crucial to ensure that the levels of residual acrylamide in PAM products are kept as low as possible to mitigate any health risks.

Industries using polyacrylamide must adhere to strict regulatory standards to ensure environmental safety. This includes monitoring and controlling the release of acrylamide into the environment and ensuring that PAM products meet safety guidelines.
The demand for polyacrylamide is expected to grow as industries continue to seek efficient and sustainable solutions. Advances in polymer technology may lead to the development of new forms of PAM with enhanced properties, expanding its applications even further.
Research is ongoing to improve the efficiency and environmental compatibility of polyacrylamide. Innovations such as bio-based PAM and advanced polymerization techniques hold promise for creating more sustainable and effective polyacrylamide products.
Polyacrylamide is a vital polymer with diverse applications across various industries. Its ability to act as a flocculant, soil conditioner, and viscosity enhancer makes it an invaluable asset in water treatment, agriculture, oil recovery, and more. While its benefits are significant, responsible production and use are essential to minimize environmental impact. As technology advances, the future of polyacrylamide looks promising, with potential for even broader applications and improved sustainability.
Understanding the applications of polymer acrylamide is crucial for those in industries that rely on its unique properties. Whether you're involved in water treatment, agriculture, or any other field that utilizes PAM, staying informed about its uses and developments can help you make the most of this versatile polymer.