
Acrylamide is a fascinating compound that plays a crucial role in various industrial and scientific applications. Despite its complex-sounding name, understanding its structure and the role of its functional groups can be quite straightforward. This article will break down the essentials of acrylamide, focusing on its structure, the role of its functional groups, and its uses in polyacrylamide production.
Acrylamide is an organic compound composed of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen atoms. It is a white, odorless crystalline solid that is soluble in water. Acrylamide is mainly used in industrial processes, particularly in the production of polyacrylamides, which are important in water treatment and other applications.
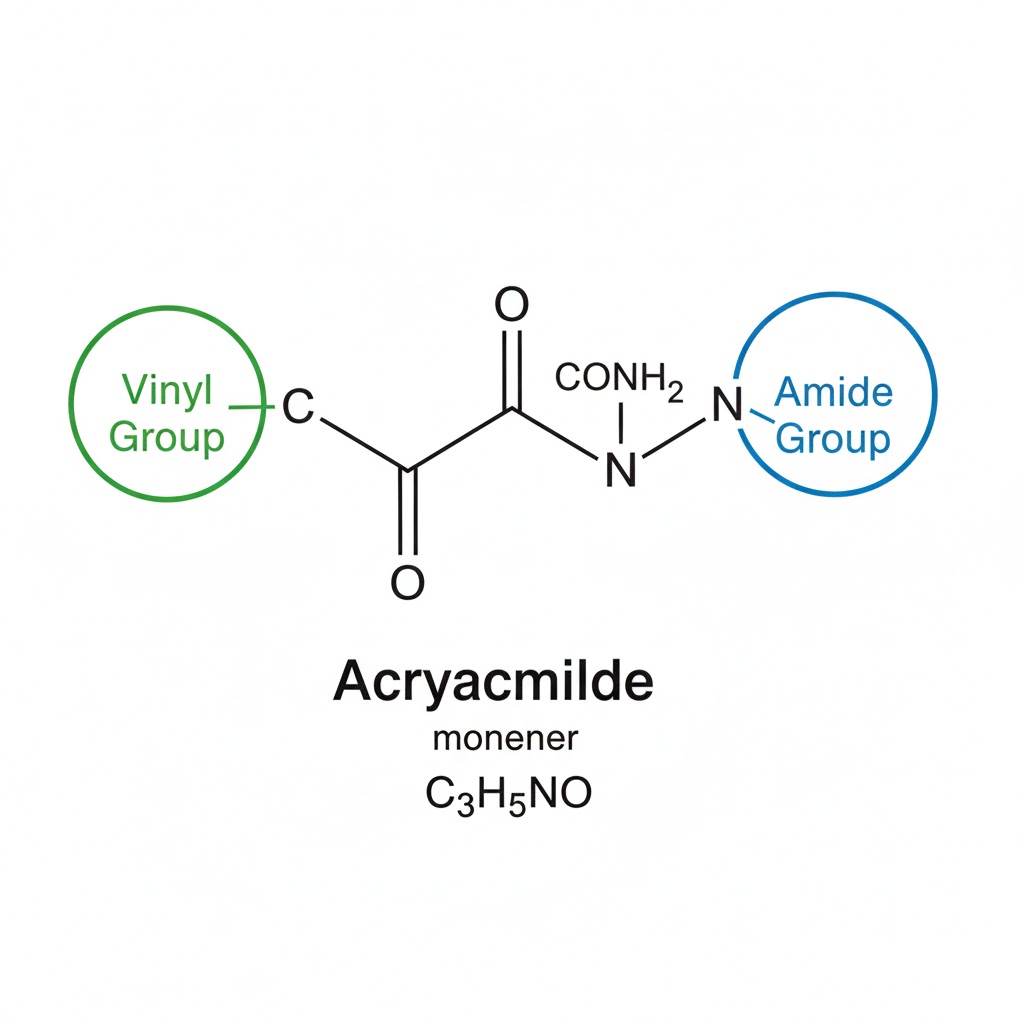
Acrylamide's chemical structure is relatively simple yet profoundly influential. The compound is made up of a vinyl group and an amide group, each contributing distinct properties that make acrylamide versatile. The combination of these groups allows acrylamide to participate in a variety of chemical reactions, making it a cornerstone in polymer chemistry.
Acrylamide, as a solid, is characterized by its high solubility in water. This property is particularly beneficial for its use in various aqueous environments. Its crystalline nature makes it easy to handle and measure, which is advantageous for industrial applications where precision is critical. Despite its odorless nature, it's important to note that acrylamide should be handled with care due to its potential health risks.
The industrial significance of acrylamide cannot be overstated. Its role in the production of polyacrylamides is pivotal. These polymers are essential in various industries, including water treatment, paper manufacturing, and oil recovery. Understanding the role of acrylamide in these processes is crucial for appreciating its contribution to modern industrial practices.
The structure of acrylamide consists of a vinyl group attached to an amide group. This configuration gives acrylamide unique properties that are valuable in various chemical reactions.
The vinyl group in acrylamide is a simple hydrocarbon group that contains a carbon-carbon double bond. This double bond is highly reactive, which makes acrylamide a useful building block in polymer chemistry. The vinyl group’s ability to undergo polymerization is what makes acrylamide so valuable, allowing it to form long chains that are essential for creating various polymers.
The amide group contains a carbonyl group (C=O) linked to a nitrogen atom. This functional group is crucial for forming hydrogen bonds, influencing the solubility and reactivity of acrylamide. The hydrogen bonding capability of the amide group enhances the stability of acrylamide in aqueous solutions, which is particularly beneficial in applications like gel electrophoresis.
The interaction between the vinyl and amide groups in acrylamide is what imparts its distinctive properties. The vinyl group’s reactivity paired with the amide group’s stability creates a compound that is both versatile and stable. This interaction is fundamental to acrylamide’s role in forming polyacrylamides, which have widespread applications in various industries.
The functional groups in acrylamide are vital in determining how it interacts with other substances. Here's a closer look at each functional group's role:
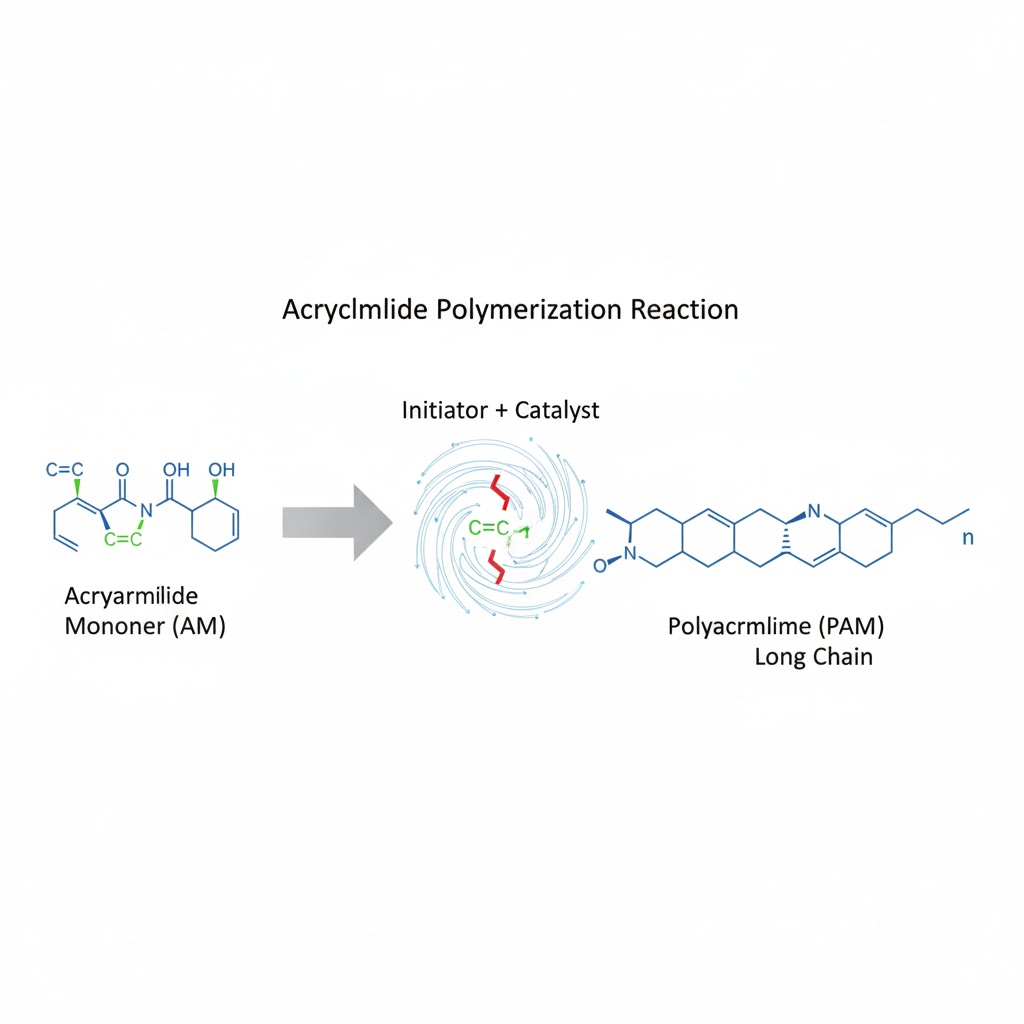
The vinyl group's carbon-carbon double bond is what makes acrylamide reactive. In the presence of certain catalysts or initiators, this bond can open up to form new bonds with other molecules. This reactivity is essential for the polymerization process, where acrylamide molecules link together to form long chains known as polyacrylamides. The ability to form these long chains is crucial for creating materials with desirable properties, such as high tensile strength and durability.
The presence of catalysts or initiators can significantly enhance the reactivity of the vinyl group. These substances facilitate the opening of the carbon-carbon double bond, allowing for the formation of new molecular structures. This process is critical in the synthesis of polymers, where the initiation phase determines the polymer's final characteristics and applications.
The amide group is crucial for the stability and solubility of acrylamide in water. The carbonyl group within the amide can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules, making acrylamide soluble. This solubility is important for its use in aqueous solutions, such as in gel electrophoresis, where polyacrylamide gels are used to separate proteins or nucleic acids. The solubility also aids in the material's functionality across various chemical environments, enhancing its versatility.
Hydrogen bonding is a key feature of the amide group, playing a significant role in the physical properties of acrylamide. These bonds not only affect solubility but also influence the compound’s thermal and mechanical stability. In applications like gel electrophoresis, hydrogen bonds contribute to the formation of a stable matrix that can effectively separate biomolecules based on size.

Acrylamide's unique structure and properties make it highly valuable in various applications, particularly in the production of polyacrylamides. Let's explore some of these applications:
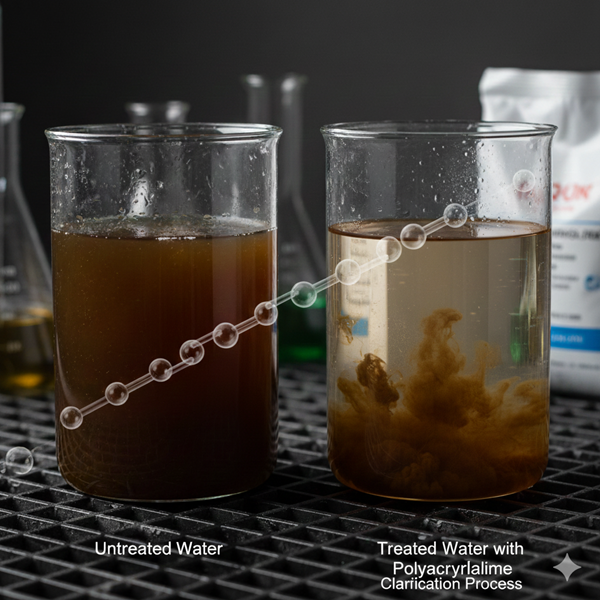
Polyacrylamides are widely used in water treatment processes. They act as flocculants, helping to aggregate suspended particles in water, which can then be removed more easily. This process is essential for purifying drinking water and treating wastewater. By improving the efficiency of particle removal, polyacrylamides help ensure the safety and quality of water supplies, which is crucial for public health and environmental protection.
The mechanism of flocculation involves the bridging of particles through the long-chain structure of polyacrylamides. This bridging action causes particles to clump together, forming larger aggregates that settle more easily out of suspension. The effectiveness of this process is influenced by factors such as the molecular weight of the polyacrylamide and the conditions of the water being treated.
In the field of molecular biology, polyacrylamide gels are used in electrophoresis to separate proteins and nucleic acids based on size. The gel's uniform pore size allows for high-resolution separation, making it a popular choice for researchers. This precision in separation is critical for various research applications, including genetic analysis and protein characterization.
The electrophoretic separation process relies on the gel matrix formed by polyacrylamides. This matrix provides a consistent environment that facilitates the movement of molecules under an electric field, allowing them to be separated based on size and charge. The clarity and resolution achieved in this process are vital for accurate molecular analysis and research outcomes.
In the oil industry, polyacrylamides are used in enhanced oil recovery techniques. They help improve the viscosity of water used to push oil out of reservoirs, increasing the amount of oil that can be extracted. This application is crucial for maximizing the efficiency and economic viability of oil extraction processes, particularly in mature or challenging reservoirs.
The mechanism by which polyacrylamides enhance oil recovery involves their ability to increase the viscosity of the water injected into oil reservoirs. This increased viscosity improves the sweep efficiency of the water, allowing it to displace more oil and thus increase the overall recovery rate. The use of polyacrylamides in this context is an example of how chemical engineering can optimize natural resource extraction.

Polyacrylamides are also used in the textile and paper industries as sizing agents, helping to improve the quality and durability of textiles and paper products. In textiles, they aid in binding dyes and improving fabric strength, while in paper production, they enhance the paper's texture and resistance to wear. These applications highlight the versatility of polyacrylamides in enhancing material properties across various industries.
As sizing agents, polyacrylamides interact with fibers and other materials to modify their surface properties. This interaction can enhance the material's resistance to water, improve its dimensional stability, and increase its overall durability. The effectiveness of polyacrylamides in these roles underscores their importance in manufacturing processes where material quality and longevity are paramount.
While acrylamide and its derivatives are highly useful, it's important to handle them with care. Acrylamide is classified as a probable human carcinogen, meaning it could potentially cause cancer. Therefore, industries using acrylamide must follow strict safety protocols to minimize exposure.
When working with acrylamide, it's essential to wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves, goggles, and lab coats. This equipment helps to prevent skin contact and protect against accidental splashes or spills. Ensuring that PPE is worn correctly and consistently can significantly reduce the risk of exposure and enhance overall safety in the workplace.
Proper ventilation is crucial in areas where acrylamide is used to prevent the inhalation of fumes. Laboratories and industrial settings should have efficient exhaust systems to maintain air quality. Additionally, handling practices should emphasize minimizing direct contact with the compound, using tools and techniques that reduce the potential for spills and contamination.
Disposal of acrylamide and its byproducts must be conducted in accordance with environmental regulations to prevent contamination of soil and water sources. Industries should implement waste management protocols that ensure acrylamide is neutralized or contained effectively. By adhering to these guidelines, companies can mitigate the environmental impact of their operations and contribute to sustainable practices.
Understanding acrylamide's structure and the role of its functional groups helps us appreciate its versatility and importance in various industries. From water treatment to molecular biology, acrylamide and polyacrylamide are indispensable in modern science and industry.
By recognizing the properties of its functional groups, we can better understand how acrylamide interacts with other compounds and how it can be safely and effectively used. Whether you're a student, researcher, or industry professional, grasping the basics of acrylamide can enhance your understanding of its applications and significance.
As research and technology advance, the applications of acrylamide and polyacrylamide are likely to expand. Innovations in polymer chemistry may lead to the development of new materials with enhanced properties, broadening the scope of their use. Understanding the foundational chemistry of acrylamide will be crucial for those looking to contribute to or benefit from these advancements.
In summary, acrylamide's vinyl and amide groups are central to its reactivity and usefulness, making it a key player in many chemical processes. Keep these insights in mind as you explore or work with acrylamide in your field. By understanding its structure and functions, you can leverage its properties to achieve desired outcomes in various applications.