
Overview of PAM Flocculants
Benefits of Anionic PAM in Water Treatment
How PAM Flocculation Works
Applications of PAM Flocculants
Selecting the Right PAM Flocculant
Why Choose Tairan Chemical PAM
Get a Quote / Contact Us
Polyacrylamide (PAM) is a high-molecular-weight, water-soluble polymer used as a flocculant in water treatment. It excels at binding fine suspended particles into larger aggregates (“flocs”) that can be easily settled or filtered out. PAM is available in anionic, cationic, and non-ionic forms (depending on its charge), each tailored to specific treatment needs. In water and wastewater systems, PAM dramatically improves solid–liquid separation efficiency, accelerating clarification and sludge dewatering. For example, high-MW PAM promotes faster sedimentation and clearer effluent by bridging particles together. Because of these properties, PAM flocculants (sometimes called “PAM chemicals for water treatment”) are widely used to improve water quality in municipal, industrial, and mining applications.
Using anionic polyacrylamide flocculant (APAM) delivers multiple advantages in water purification. Key benefits include:
Superior Clarity: Anionic PAM has strong flocculation power to capture suspended impurities. It causes very fine particles and turbidity to agglomerate into dense flocs, greatly enhancing visual clarity of treated watersinofloc.com.
Efficient Solids Removal: By forming large settleable flocs, APAM enables faster solid–liquid separation. This simplifies filtration and helps achieve regulatory clarity targets more reliably.
Reduced Chemical Usage: High-efficiency PAM flocculants cut the need for excess coagulants. Industry reports note that polyacrylamide use “reduces the consumption of additional chemical products and reduces process times,” translating into significant energy and cost savings. In practice, APAM can shorten treatment cycles, lower power/chemical bills, and extend equipment life.
Lower Operating Costs: Improved flocculation means fewer treatment stages and less reprocessing. Plants using anionic PAM often see measurable cost reduction because less polymer is needed overall and filter media last longer.
Environmentally Friendly: By minimizing waste and chemical byproducts, modern PAM formulations support sustainable operation. They help meet environmental standards by lowering sludge volumes and reducing residual toxicity. (For best results, choose a high-purity PAM that meets all water-quality regulations.)
In summary, anionic PAM acts as a value-added flocculant: it boosts water quality while cutting energy and chemical requirements.
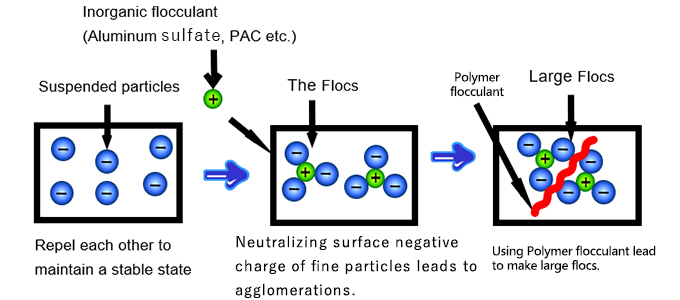
Polyacrylamide works by a two-step process in water treatment: coagulation followed by flocculation. Initially, PAM neutralizes or compresses the electric charge on particles, causing micro-flocs to form. Then the polymer chains bridge between particles, binding them into larger, denser flocs. Because PAM molecules are long chains with repeating acrylamide units, they can wrap around and interlock particles, creating mesh-like flocs that settle quickly.
This bridging/adsorption action is especially effective for very fine or colloidal solids. In practice, a small dose of anionic PAM added to wastewater immediately begins to aggregate impurities. As the flocs grow, settling accelerates – clarifiers and settling tanks can operate more efficiently. The result is faster removal of suspended solids and reduced turbidity. In sludge dewatering, PAM-treated sludge forms drier cakes that are easier to handle and dispose of.
Proper mixing and dosing are key: PAM must be dissolved in clean water and added gradually. When correctly applied, PAM flocculants dramatically improve separation without introducing toxic chemicals (modern PAM is safe when properly used).
Polyacrylamide flocculants are used in virtually every water and wastewater application where solids removal is needed. Typical industries and processes include:
Municipal Wastewater Treatment: PAM aids sedimentation of sewage and sludge dewatering. It accelerates settling in primary clarifiers and improves sludge filterability, producing cleaner effluent.
Industrial Effluents: In textile, chemical, food & beverage, and paper mills, PAM is used to clarify process water and effluent. It removes dye particles, organics, and suspended matter before discharge or recycling. In papermaking, PAM increases fiber retention and enhances wastewater settling.
Mining and Mineral Processing: Tailings and acid-mine drainage often have very fine solids. Anionic PAM flocculants quickly settle the slurry solids in thickeners, producing clear overflow water and dense underflow that is easier to dewater.
Oil & Gas: PAM is used in water-based drilling fluids and enhanced oil recovery (EOR). It improves fluid viscosity and solid control, enabling separation of cuttings and particulates in produced water.
Agriculture & Food Processing: PAM helps clarify irrigation runoff and wash water. For example, in sugar processing, PAM is added to settling tanks to purify cane-juice by flocculating suspended impurities.
Other Applications: Any high-turbidity or high-solid stream – such as landfill leachate, printing wastewater, or even drinking water treatment – can benefit from PAM flocculants.
Each application may require a different PAM charge or molecular weight. For example, the sugar industry uses PAM in syrup clarification and condensate cleaning, while dyeing operations may combine PAM with inorganic coagulants to remove color and solids.
Choosing the optimal PAM for a given water treatment scenario depends on several factors: charge (ionicity), molecular weight, dosage, and water chemistry. A few guidelines:
Ionic Charge: Anionic PAM (APAM) carries negative charge and is generally best for waters with suspended inorganic solids (e.g. clay, silica) and particles that are neutral or positively charged. Cationic PAM (CPAM) is preferred for sludge or wastewater high in organic colloids (like in papermaking or municipal sludge) because its positive charge binds organic matter. Non-ionic PAM (NPAM) can be useful when neither strong positive nor negative charge is needed, such as in certain soil or groundwater applications. Tairan’s product literature notes that “APAM – ideal for municipal and industrial wastewater treatment, especially to remove suspended solids”, while “CPAM – often used in sludge dewatering and oil recovery”.
Molecular Weight & Structure: Higher molecular weight PAM chains generally produce stronger bridging and larger flocs. Linear high-MW PAM is often used when minimal dosage is desired. Branched or cross-linked structures may be chosen for very fast formation of robust flocs. Tairan Chemical offers PAM from about 5–20+ million Da to suit different viscosities and floc strengths.
Dosage & Testing: A Jar-test or pilot trial should determine the exact dose. Typical polymer dosages range from 1 to 10 mg/L depending on water quality. Always dissolve PAM slowly in clean water to the manufacturer’s recommended concentration (e.g. 0.1–0.5%) before adding to the treatment stream.
pH and Coagulants: Anionic PAM works well over a wide pH range but often is paired with coagulants (like alum or polyaluminium chloride) in soft or highly acidic/alkaline waters. Adjusting pH and adding a coagulant can improve performance when treating challenging effluents.
For complex wastewater, Tairan’s technical team can help select the best PAM grade. We offer a full range of Anionic, Cationic, and Non-Ionic PAM products, each tailored for specific TSS removal, dye binding, or sludge dewatering needs.

Tairan Chemical is a leading supplier of high-quality PAM flocculants for water treatment. Our advantages include:
Proven Quality: We manufacture PAM under strict quality control to meet international standards. Each batch is tested for molecular weight and purity to ensure consistent performance. Our products meet GB/T and ASTM specifications for water treatment polymers.
Wide Range of Grades: Tairan offers custom solutions with varied charge density, molecular weight (5–20+ million Da), and physical form (granules, powder, emulsions). Whether you need a strongly anionic powder for sewage treatment or a specialty neutral polymer, we have the right grade.
Technical Expertise: Our technical service helps customers optimize dosing and application. We provide guidance on Jar-tests, dissolution methods, and combination with other coagulants. You can learn more about Tairan PAM products or review our APAM product data for detailed specs.
Cost-Effective Supply: Tairan Chemical offers competitive pricing for bulk PAM orders. Our efficient manufacturing and logistics ensure you receive large quantities on schedule. Quality and economy go hand-in-hand – our customers enjoy lower overall treatment costs thanks to PAM’s high efficiency.
Sustainability Commitment: We continually develop eco-friendlier formulations. By choosing our PAM flocculants, you benefit from a solution that minimizes sludge and chemical residues, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Partnering with Tairan Chemical means access to industry-leading polyacrylamide (PAM) solutions. Whether you call it “anionic polyacrylamide flocculant” or “PAM for water treatment,” our products are engineered to deliver results. From design to delivery, our team provides responsive support – Get a Quote or Contact Us to discuss your requirements.
Ready to improve your water treatment processes? Tairan Chemical PAM specialists are here to help. Contact our sales team for pricing, sample testing, or technical consultation. You can Get a Quote or Contact Us any time for bulk orders of polyacrylamide. We’ll work with you to ensure you select the optimal anionic PAM flocculant for your project.