Top 7 Benefits of Using Polymeric Aluminium Chloride (PAC) in Water Purification
Polyaluminium chloride (PAC) is a high-charge, inorganic polymeric coagulant valued for fast clarification, broad pH compatibility, and low sludge yield. Compared with traditional alum or ferric salts, modern PAC grades—especially white, low-insoluble powder—deliver clearer water at lower dosages and with simpler operations. For product specifics (28–30% Al2O3, CAS 1327-41-9), see our Polymeric Aluminum Chloride (PAC) product page.
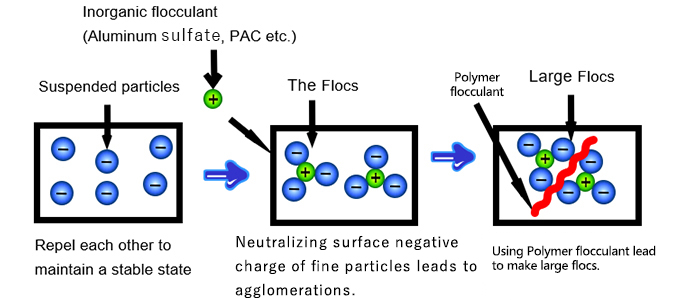
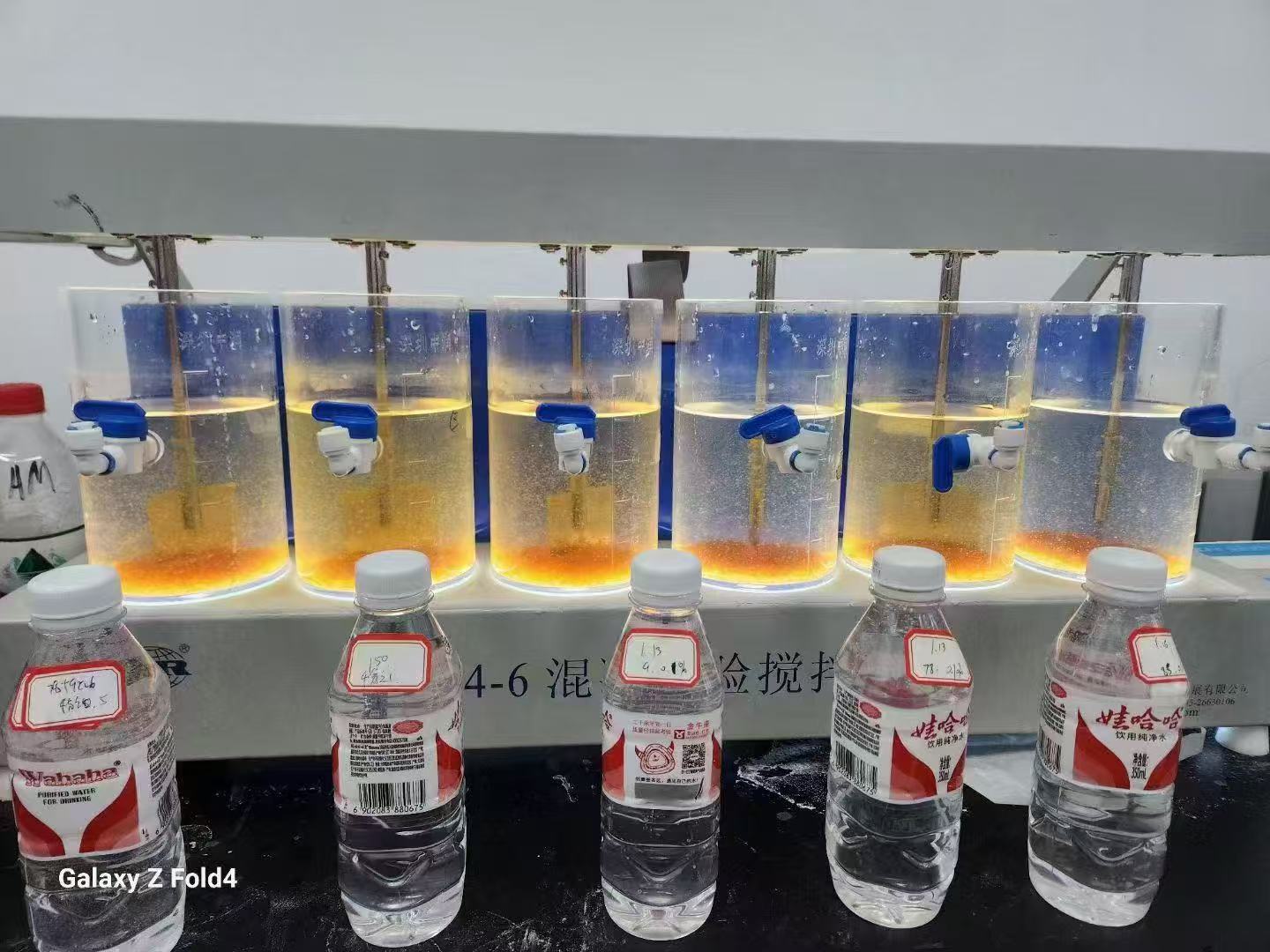
1) High Coagulation Efficiency at Lower Dosage
PAC’s polymerized Al-hydroxy species rapidly neutralize negatively charged colloids and natural organic matter, forming dense, settleable flocs. In practice, plants often achieve target turbidity with lower PAC dosages than with alum, improving chemical cost per m3. For typical use cases and jar-test tips, refer to Why PAC is the most effective coagulant.
2) Broad pH Window & Fewer Adjustments
PAC performs across a wide pH (≈5–9), often reducing the need for lime/acid trim and simplifying control in variable raw waters common in monsoon and arid regions.
3) Rapid Floc Formation & Shorter Clarification Time
High charge density promotes fast microfloc formation, enabling shorter flocculation times and higher clarifier throughput. This supports compact retrofits and capacity debottlenecking without major CAPEX.
4) Lower Sludge Volume & Easier Dewatering
PAC typically generates denser, lower-volume sludge than conventional salts, cutting hauling and disposal costs. Dewatering with belt press or filter press is more consistent due to stronger, more shear-resistant flocs.
5) Stable Performance in Low-Temperature or Colored Waters
White PAC grades maintain coagulation kinetics in colder raw water and in high-color surface sources—common challenges in upland catchments and peat-influenced rivers.
6) Cleaner Finished Water (Low Residuals)
Optimized PAC dosing achieves low residual aluminum and minimal sulfate/chloride addition compared with some legacy coagulants, supporting potable and process-water specs. See our application notes: PAC Powder: Uses & Best Practices.
7) Total Cost of Ownership Advantage
Lower dose, fewer pH corrections, reduced sludge, and higher plant uptime compound into a measurable TCO benefit. This is especially attractive for industrial users where chemical, energy, and disposal costs impact unit production economics.
Where PAC Excels
Municipal drinking water: Turbidity/color removal, seasonal swings, cold water.
Industrial wastewater: Mining fines, aggregate wash water, textile dye removal, food & beverage, petrochemical.
Process water pre-treatment: RO/NF feed conditioning to protect membranes.
For a step-by-step selection and dosing guide, bookmark our PAC Water Treatment Guide.
Practical Engineering Notes
Jar testing: Optimize coagulant dose, mixing G-values, and flocculation time; confirm pH setpoint before scale-up.
Make-down: For powder, prepare 5–10% stock; dilute to 1–2% for dosing. Use corrosion-resistant wetted parts.
Typical dose: 10–60 mg/L for surface water; industrial effluent varies—always validate by jar test.
Compatibility: Can be coupled with anionic polyacrylamide as a flocculant aid to strengthen and grow flocs.
Specify the Right PAC for Your Plant
Compare our standard 28–30% PAC grades and request regional pricing (Southeast Asia & Middle East) on the PAC product page. Need dosing help? See: Why PAC Works and PAC Powder Uses.
Looking for flocculant aids to pair with PAC? Explore Anionic Polyacrylamide (APAM) and other water treatment polymers.
Illustrations




PAC FAQs
What dose of PAC should I start with?
For surface waters, 10–60 mg/L is a common screening range. Always confirm by jar testing to fine-tune dose, mixing, and pH.
Is PAC suitable for drinking water?
Yes—high-purity PAC grades are widely used in potable water clarification and routinely meet residual aluminum limits when correctly dosed.
Can PAC be combined with polymer flocculants?
Yes. Pairing PAC with anionic polyacrylamide often improves floc size/strength and dewatering performance.








