
PAM polymers, or polyacrylamides, are remarkable materials with diverse applications. They are known for their water-absorbing abilities, making them essential in many industries.
These polymers play a crucial role in water treatment, agriculture, and even consumer products. Their versatility allows them to address various environmental and industrial challenges.
Understanding the different types of PAM polymers, such as anionic and cationic, is key to leveraging their full potential. Each type has unique properties and applications, enhancing their utility.
Super absorbent polymers, a subset of PAM, are particularly notable for their high water retention. They are used in products ranging from diapers to agricultural aids.
As the demand for efficient and sustainable solutions grows, PAM polymers continue to evolve. Their expanding role in modern industries highlights their importance in addressing global needs.
PAM polymer, also known as polyacrylamide, is a synthetic polymer with diverse uses. It is made by polymerizing acrylamide monomers. This process creates long chains with water-absorbing properties, making it valuable in various settings.
Polyacrylamide is available in multiple forms, including powders, beads, and emulsions. This variety allows it to meet different industrial needs effectively. Its adaptability makes it a favored choice in numerous applications.
The chemical formula for polyacrylamide is (C3H5NO)n. This formula represents the repeating units that form the polymer chain. The simplicity of the formula belies the complexity and versatility of this material.
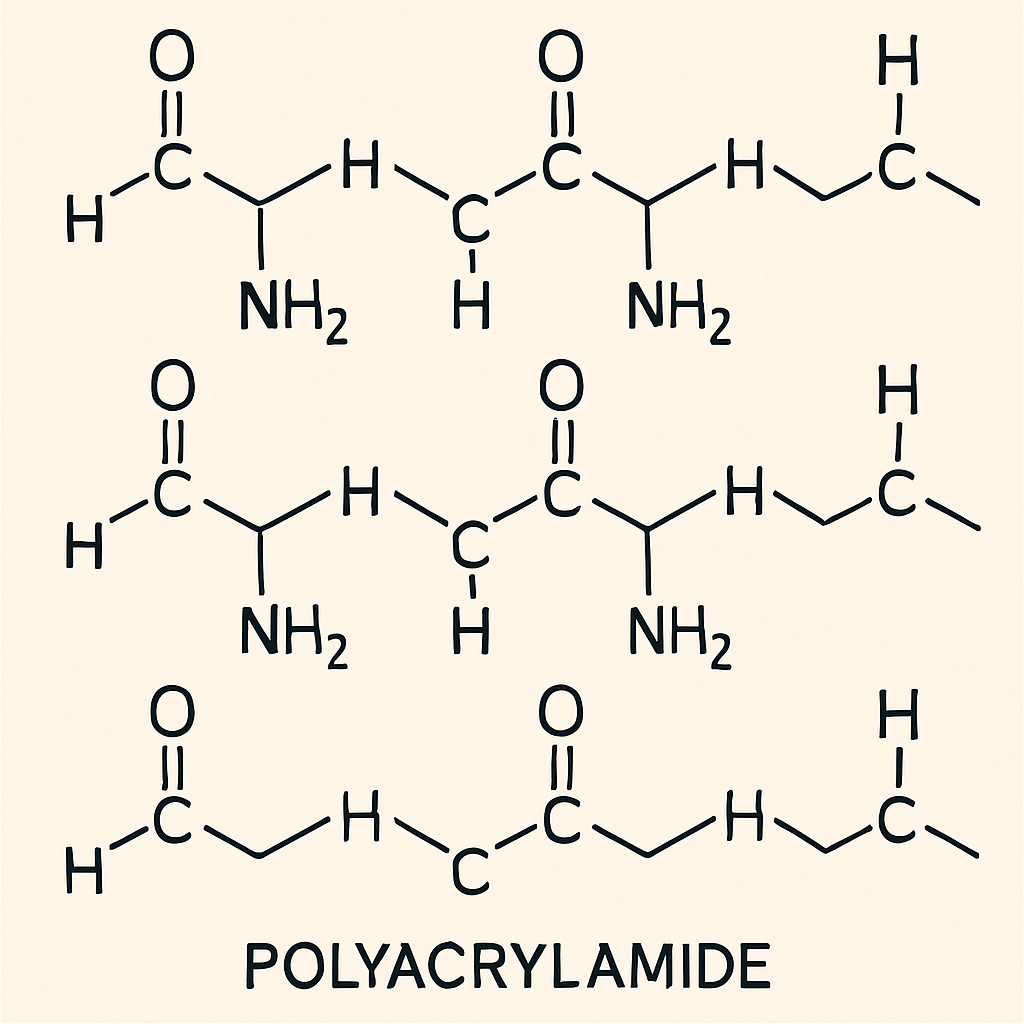
Key features of polyacrylamide include:
●High water solubility
●Robust gel-forming abilities
●Environmentally friendly when used correctly
These features highlight polyacrylamide's versatility in industrial, environmental, and consumer applications. Understanding its properties allows researchers and industries to leverage it effectively.
Polyacrylamide's chemical structure is straightforward yet versatile. It consists of repeating acrylamide units forming long chains. This structure can be modified for specific uses.
The polymer is categorized into several types based on its ionic nature. These include anionic, cationic, and non-ionic forms. Each type has unique properties and applications.
Anionic polyacrylamide is often used in water treatment as a flocculant. It effectively removes suspended particles from water systems. Cationic polyacrylamide is useful in sludge dewatering and paper production due to its binding properties.
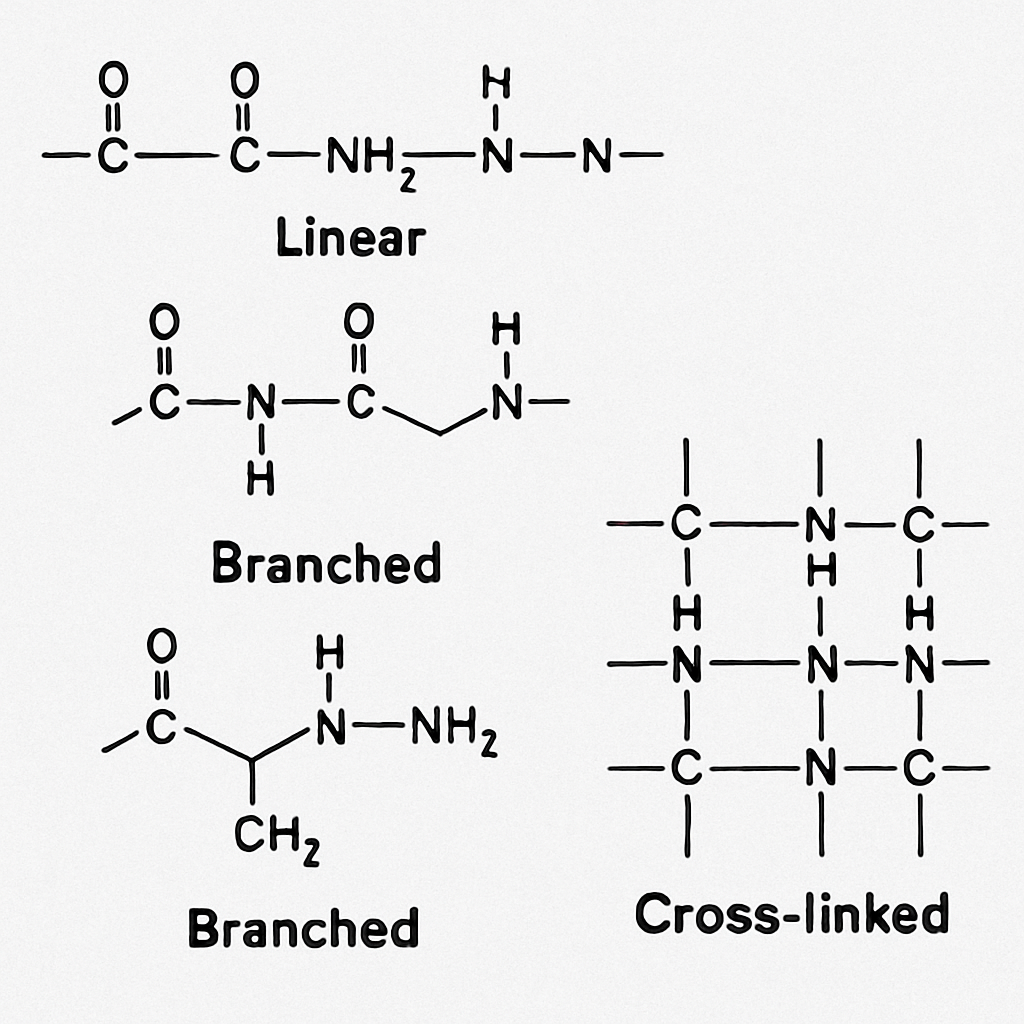
Key types of polyacrylamide include:
Each type addresses distinct industrial needs. The availability of these variations enhances the polymer's adaptability. Understanding polyacrylamide's types helps in selecting the right material for specific challenges.
The main difference between anionic and cationic polyacrylamide is their charge. Anionic polyacrylamide carries a negative charge, while cationic polyacrylamide holds a positive charge. This distinction influences their behavior in various applications.
Anionic polyacrylamide is ideal for treating wastewater with positively charged particles. It is often used in industries needing enhanced solid-liquid separation. The polymer's negative charge attracts positively charged particles, facilitating flocculation.
Cationic polyacrylamide is preferred when the target particles are negatively charged. This includes processes like sludge dewatering and improving paper quality. Its positive charge helps bind with these negatively charged substances efficiently.

Here’s a quick rundown of their applications:
●Anionic: Water treatment, soil erosion control, enhanced oil recovery.
●Cationic: Sludge dewatering, papermaking, textile processing.
These charge characteristics make them indispensable in various sectors. Choosing the correct polyacrylamide type enhances the efficacy of industrial processes. Understanding these differences is crucial for optimal application.
Super absorbent polymers (SAP) are renowned for their impressive water retention abilities. These absorbent polymers can hold many times their weight in water. This remarkable feature makes them invaluable in various industries.
SAP polymers are widely used in personal care products like diapers and sanitary pads. Their ability to trap moisture keeps the skin dry and comfortable. This contributes significantly to consumer satisfaction and product effectiveness.
In agriculture, SAP plays a vital role in water conservation. These polymers help retain moisture in soil, enhancing plant growth even in arid conditions. They provide an innovative solution to reducing water usage in farming.

Some common applications of SAP include:
●Diapers and hygiene products
●Agricultural water retention
●Biomedical devices
●Spill control products
Additionally, SAP polymers find use in medical field applications. They are employed in wound dressings and other moisture-managing products. Their versatility is key to solving diverse challenges across industries.
PAM polymers, particularly polyacrylamides, showcase remarkable versatility. Their unique properties enable a broad range of industrial applications. Let's explore some key industries where PAM polymers make a significant impact.
In the water treatment sector, anionic polyacrylamide is an effective flocculant. It efficiently removes suspended particles, helping to clarify water. This application is essential for both municipal and industrial wastewater treatment.
The oil recovery industry also benefits from PAM polymers. They enhance oil extraction by improving water viscosity, boosting efficiency. This leads to increased oil yields and decreased resource wastage.
Other notable applications include:
●Paper manufacturing
●Textile processing
●Mineral processing
●Dust control
●Soil stabilization
In the paper and pulp industry, PAM polymers improve paper quality. They help in bonding fibers and reducing paper porosity. This results in stronger, higher-quality paper products.
Moreover, PAM polymers are used in mining to separate valuable minerals efficiently. By helping to extract minerals, they contribute to reduced costs and increased sustainability. Overall, PAM polymers' adaptability makes them indispensable across diverse industries.
PAM polymers play a crucial role in water treatment and environmental sustainability. Their ability to absorb and clarify makes them ideal for purification processes. These polymers are utilized extensively in municipal and industrial settings to enhance water quality.
Anionic polyacrylamide, in particular, is highly effective in treating wastewater. It aggregates fine particles, facilitating their removal from water. This process is vital for reducing water turbidity and improving clarity.
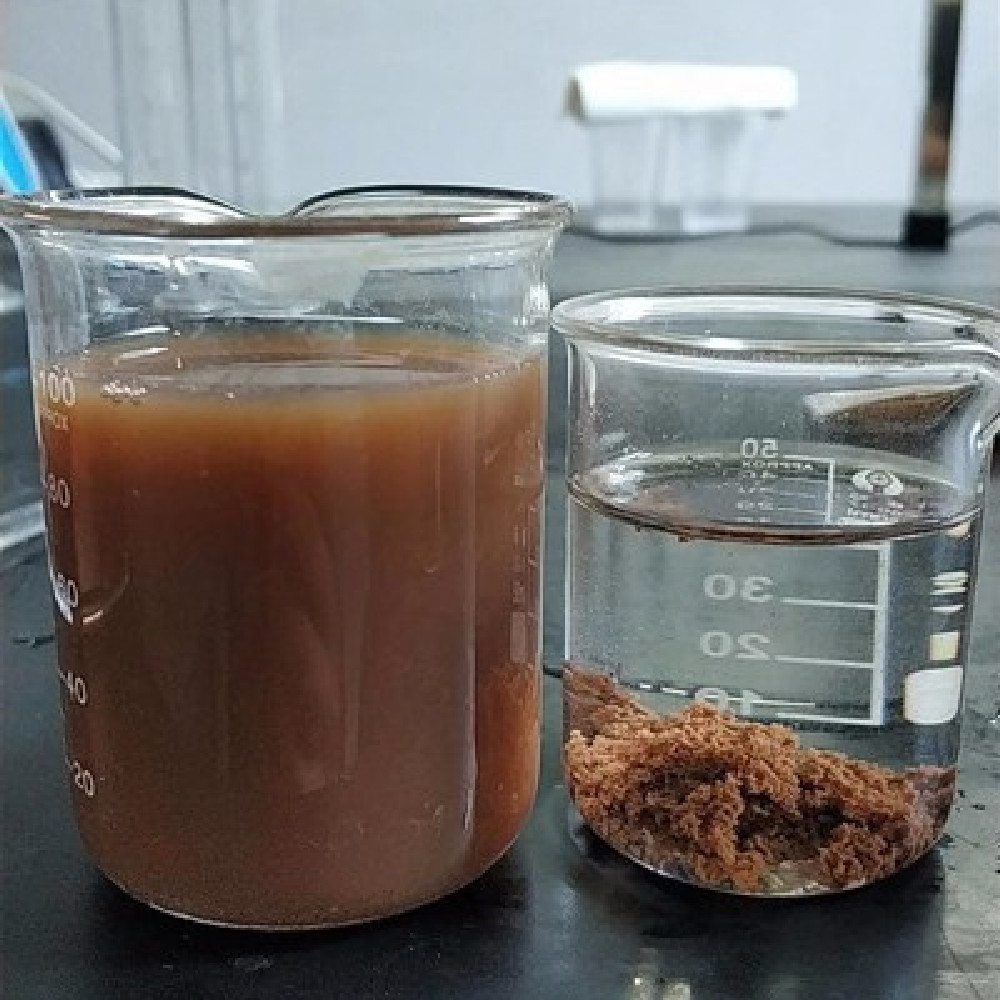

In environmental protection, PAM polymers contribute to soil and water conservation. Their use in stormwater management helps mitigate runoff and erosion. By stabilizing soil, they prevent sediment from entering waterways.
The benefits of PAM polymers in this field include:
●Reducing soil erosion
●Improving water infiltration
●Enhancing soil structure
●Decreasing water turbidity
Additionally, PAM polymers enhance filtration systems, providing safer drinking water. They are biodegradable under certain conditions, reducing environmental impact. Their safety and effectiveness make them a preferred choice for sustainable solutions.
Overall, the integration of PAM polymers into water treatment and environmental practices highlights their importance. They provide efficient, cost-effective, and eco-friendly options for preserving our precious water resources.
PAM polymers have transformed agricultural practices through improved water management. By enhancing soil structure, they help retain moisture, which is crucial for crop health. This capability leads to more efficient water use, improving yield and reducing waste.
In mining, PAM polymers facilitate mineral separation. They optimize the process by aggregating fine particles, improving extraction efficiency. This application not only boosts productivity but also reduces energy consumption.
Oil recovery benefits significantly from PAM polymers. They enhance the viscosity of water injected in secondary recovery processes. This results in increased oil extraction rates, maximizing resource utilization.
Key advantages of PAM in these sectors include:
●Efficient water usage in agriculture
●Enhanced mineral recovery
●Improved oil extraction rates
Innovative applications of PAM polymers continue to expand, with ongoing research aimed at optimizing formulations. Their role in these industries exemplifies their versatility and importance in sustainable practices.
Polyacrylamide finds wide use in many consumer products due to its beneficial properties. In cosmetics, it stabilizes formulations and thickens products for better consistency. This versatility makes it an essential ingredient in creams, lotions, and gels.
In the medical field, polyacrylamide is significant for its unique water-absorbing capabilities. It's utilized in wound care products to manage fluids effectively. Its non-toxic nature ensures safety in sensitive medical applications.
Key applications of polyacrylamide in these sectors include:
●Thickening cosmetics
●Stabilizing personal care products
●Fluid management in medical dressings
The adaptability of polyacrylamide enhances its role in developing innovative consumer and medical products. Its widespread usage underscores the material’s importance in daily life and healthcare.
PAM polymers exhibit minimal environmental impact when used responsibly. Their biodegradable properties reduce long-term pollution risks. This makes them a safer choice for various applications.
Ensuring safe practices involves correct usage and disposal methods. This is crucial in minimizing potential environmental harm. Polyacrylamide's non-toxic nature enhances its safety profile in industrial and environmental contexts.
Important considerations for environmentally friendly use include:
●Correct application techniques
●Proper disposal methods
●Eco-friendly formulations
By prioritizing these practices, industries can leverage PAM polymers' benefits while safeguarding environmental health. Innovation continues to optimize PAM formulations, further increasing their eco-friendliness.
The market for PAM polymers is expanding rapidly. Demand for water treatment solutions and eco-friendly options fuels growth. Industries seek efficient ways to manage water resources and reduce waste.
Innovation plays a key role in this growth. Researchers focus on developing new polymer formulations. These aim to enhance performance and environmental compatibility.
Emerging trends and innovations include:
●Advanced eco-friendly formulations
●Enhanced biodegradability
●Improved polymer synthesis techniques
These innovations position PAM polymers as solutions in modern industrial applications. As demand increases, continued research will drive future advancements. This ensures PAM's relevance in addressing global challenges.
PAM polymers, with their versatile applications, are crucial across diverse industries. Their ability to absorb and retain water makes them indispensable for water treatment and environmental protection.
As technology advances, their role continues to evolve. Innovations focus on enhancing their efficiency and reducing environmental impact. This adaptability ensures that PAM polymers remain vital in addressing both current and future industrial challenges. As research progresses, their impact is set to grow, cementing their importance in the modern world.